Dog owners should know the difference between fungal and bacterial infections in dogs!
Every high temperature season is a time when pet owners have headaches, because it is a period of high incidence of fungal and bacterial infections, and dogs will have many skin diseases. However, the treatments for fungal infections and bacterial infections are different, so we pet owners must understand the difference between fungal and bacterial infections in dogs before treating them.
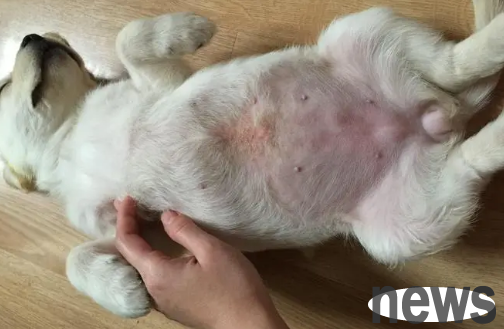
1. Fungal infection in dogs
1. Symptoms
The symptoms of fungal infection in dogs are mainly ringworm spots, hair loss, skin redness, itching, etc. Due to itching, dogs will frequently scratch the affected area with their hands, which will also cause symptoms such as redness, swelling, ulceration, etc. in the affected area, aggravating the infection.
2. Treatment methods
Currently, antifungal drugs containing terbinafine are mainly used to treat fungal infections. During the treatment period, the dog needs to be given medication on time to prevent the dog from developing drug resistance. Generally, dogs with mild symptoms can recover within 7-14 days of treatment. However, if the dog's condition is serious, it is also necessary to take a medicated bath with ivermectin ingredients. The medicated bath needs to be performed 1-2 times a week, and oral anti-inflammatory drugs are also required.
3. Precautions
Since fungal infections in dogs can be transmitted to people, when dogs are infected with fungi, they need to be isolated and fed in time to avoid infecting other animals or people in the home, and the dog’s living environment and items used need to be disinfected regularly.
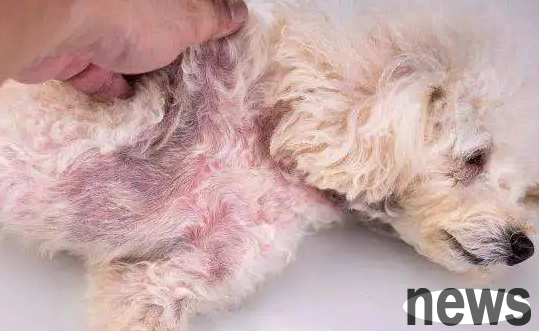
2. Bacterial infection in dogs
1. Symptoms
The symptoms of bacterial infection in dogs mainly include skin redness, itching, hair loss, and inflammation. In severe cases, there may be patches of hair loss, or even pustules all over the body.
2. Treatment methods
For dog bacterial infections, you can use some anti-inflammatory drugs, such as oral amoxicillin or cephalexin, to reduce inflammation. In addition, you can also choose to use injectable anti-inflammatory drugs, such as cefazolin, triaxone and other anti-inflammatory drugs, and you can also use some vitamin B together. The general treatment course lasts for about 7-14 days. The bacteria on the surface of the dog's skin are cleared and the skin will recover after the inflammation is controlled.
3. Precautions
Do not bathe the dog during the treatment, otherwise it may cause the dog's skin to become moist, which may in turn breed fungi and worsen skin diseases.